Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States for both men and women.1 And in 2021, cardiovascular complications were responsible for one in every five deaths, totaling nearly 700,000.1 In addition to this significant human toll, these complications place an economic burden on the nation, costing nearly $240 billion annually.1
With cardiometabolic multimorbidity becoming increasingly common, cardiometabolic risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, lack of exercise and excess alcohol consumption are contributing to the rise of conditions such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease, coronary heart disease, stroke and heart failure.2 Access to cardiometabolic diagnostic tests is crucial, with early detection and intervention essential to preventing complications and disease progression.
Advancement of cardiac biomarkers
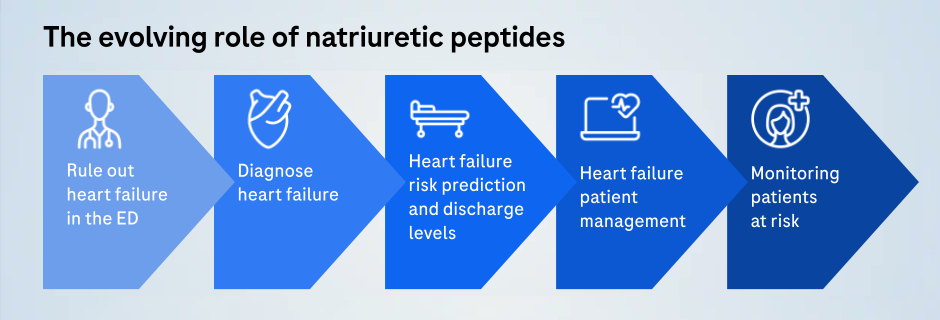
As a tool first used to diagnose acute heart failure in the emergency department, cardiac biomarkers have evolved over the past two decades.
Today, cardiac biomarkers are essential in treating and improving care for people with cardiometabolic disease, and are used for both early identification or last-minute supporting intervention. Roche has 20 years of leveraging cutting-edge biomarker technology in cardiometabolic disease diagnosis.
Our two biomarkers include Elecsys® NT-proBNP and Elecsys® Troponin T Gen 5 STAT.
Elecsys® NT-proBNP: Delivering confidence when managing heart failure
Elecsys® Troponin T Gen 5 STAT: Enabling fast diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction
As cardiac biomarkers and digital solutions evolve, we are committed to continuing research in cardiometabolic disease to advance early diagnosis and help improve clinical decisions.
Lab implications for cardiac biomarkers
In light of recent studies and updated guidelines, laboratories can likely expect an increased volume of cardiac biomarker tests. Laboratorians play a pivotal role, providing critical insights for patients, ranging from those experiencing a cardiac event to individuals undergoing routine testing.
The Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of Rapid Optimization of Heart Failure (STRONG-HF) study conducted in 2022 demonstrated the significance role of the NT-proBNP cardiac biomarker test in improving outcomes for individuals hospitalized due to heart failure. And the 2024 update of the American Diabetes Association's Standards of Care in Diabetes now advocates for the use of the NT-proBNP biomarker test for annual heart failure testing.



.png)